Why is the trachea reinforced with cartilaginous rings. Help in moving foreign bodies through the respiratory tract and help preventing infection or obstruction.

Trachea Definition Anatomy Function And More
But when you touch it and run your finger along the interior lining it slides right along and you can.
. Click here to enter text. The conducting portion includes the nasal cavity and extends through the pharynx larynx trachea bronchi and larger bronchioles. The cilia are there to trap foreign particles before they reach the lungs.
The cilia project into the channel lumen of the trachea to trap particles. In the photograph below the heart and blood vessels of the neck region have been removed so that the trachea can be seen more clearly. Due to the trachea not wanting a breakdown or corruption the cartilaginous rings are there as a support beam to negate the negative.
Describe the interior lining of the trachea. Describe the lining tissue of the respiratory tract from the external nares nostrils to the beginning of the trachea. Up to 24 cash back h Describe the appearance of the inner lining of the stomach.
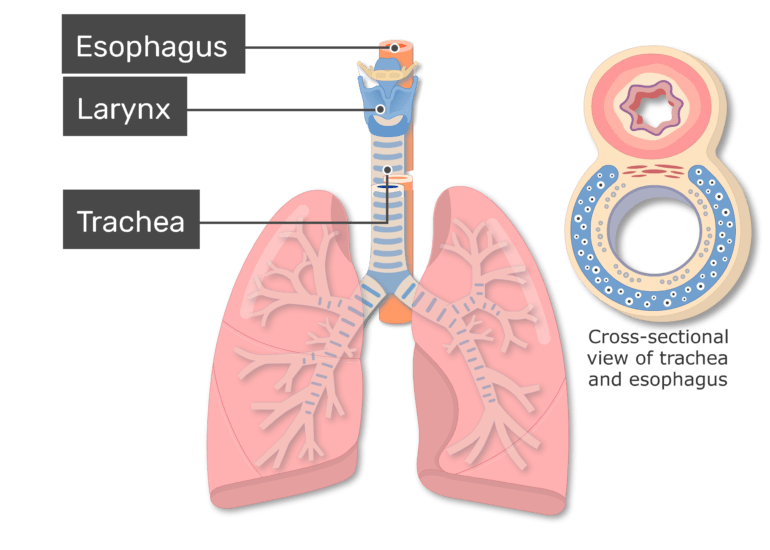
Describe the interior lining of the trachea. Describe red pulp and white pulp found in the spleen. The esophagus is dorsal to the trachea.
The mucus generated from the trachea traps the microorganisms and de is from entering into the lungs. Lining of the trachea and bronchi is associated with cilia and mucus to protect the organs. Particles getting inside respiratory tract with air are getting trapped by the mucus this prevents entry of dust particles etc.
Click here to enter text. Gretchen who is nine years old is upset because after finally persuading her daddy to play soccer with her he had to sit down and rest after only 15 minutes. Were there many or few vessels serving as conduits between the lungs and the heart.
-inner surface of the trachea is lined with pseudostratified columnar epithelium. The inner lining of the trachea is a pseudostratified columnar epithelium composed mainly of mucus-secreting goblet cells ciliated cells and short basal stem cells Figure 3. Why is the trachea reinforced with cartilaginous rings.
-surface of the cell is lined with cilia. Describe the interior lining of the trachea. Explain the significance of the alkaline mucous layer lining the interior surface of the stomach.
Tracheas inner lininglining that faces the hollow side is comprised of ciliated epithelium which rests on a basement membrane In between the ciliates cells the goblet cells are situated. Moist smooth tissue called mucosa lines the inside of the trachea. There are also cells and ducts in the mucous membrane that secrete mucus droplets and water molecules.
The mucus traps inhaled particles and the upward beating of the cilia drives the debris-laden mucus toward the pharynx where it is swallowed. The trachea is lined with a moist mucous-membrane layer composed of cells containing small hairlike projections called cilia. I couldnt even see any of the cartilage rings including on the lateral and anterior sides.
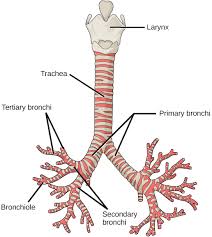
Why is this important. Trachea The trachea windpipe begins immediately below the larynx voice box and runs down the center of the neck into the thoracic cavity where it branches into two bronchi that will enter the right and left lungs. The mucus is continuously sent towards larynx by the action of cilia.
It contains the vocal cords. Correct option is C The trachea is lined with ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium a type of epithelium with goblet cells that produce mucins the main component of mucus to moisten and protect the airways from foreign particles. The trachea widens and lengthens slightly with each breath in returning to its resting size with each breath out.
To have the nasal passage attain warm air and moisturize. When viewed you just see longitudinal striationslines. 1 The inner lining of trachea is lined by a mucous membranesmooth shining membrane which helps to keep it wet and prevention from drying it is filled in a sticky material and highly viscous fluid also called as mucus.
It consists of 16-20 tracheal cartilages anterolaterally and a fibromuscular wall posteriorly. Tracheas inner lininglining that faces the hollow side is comprised of ciliated epithelium which rests on a basement membrane In between the ciliates cells the goblet cells are situated. They support the trachea and keep it open during pressure changes that accompany air ventilation.
The large hard structure attached to the trachea is the larynx. Describe the interior lining of the trachea The trachea is lined with mucous mem ane layer composed of cilia submucosa and adventitia. Describe the path a molecule of oxygen takes to get to body tissue starting with the nares.
I actually thoroughly enjoyed observing this. The trachea is a D-shaped fibrocartilaginous respiratory organ. Many little folds that look like little hills line the inside of the stomach.
The trachea is a hollow tube-like structure that runs from the larynx or voice box to the bronchi the two passageways that connect the. This type of epithelium can easily sense foreign particles and ciliary movement remove the particles. The inner lining of the stomach as viewed by the eye appears to be a dull pink--almost brown.
The interior portion of the trachea has a moist mucous membrane layer and it has cells that contain small hair-like projections called cilia. -one cell layer thick but nuclei reside at different levels so it looks like its multiple layers. Name two functions of the nasal cavity mucosa.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pre-Lab Questions 1. The tracheal cartilages are composed of hyaline cartilage and interconnected by fibroelastic tissue. She indignantly berated him saying You know.
What role do the rings of cartilage surrounding the trachea play. However underneath the microscope it is a lighter pink with a yellowish tinge.

What Is Trachea Function Structure And Purpose Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Tracheal Wall Composition And Structure Anatomy Of The Tracheal Tube Or Windpipe
0 Comments